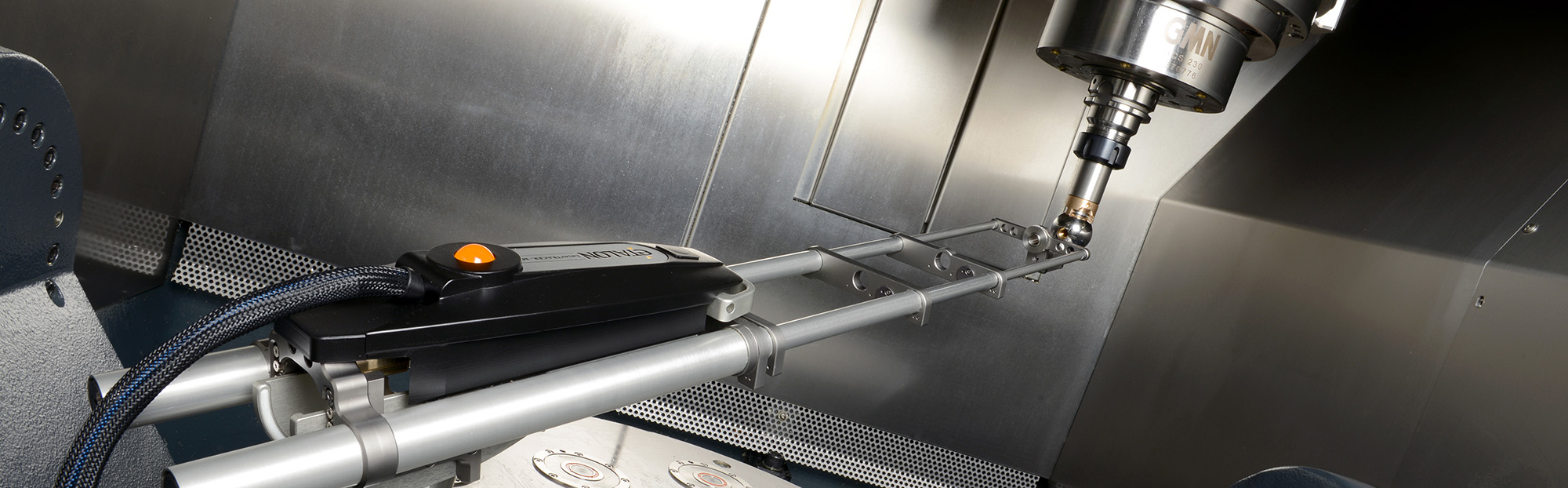
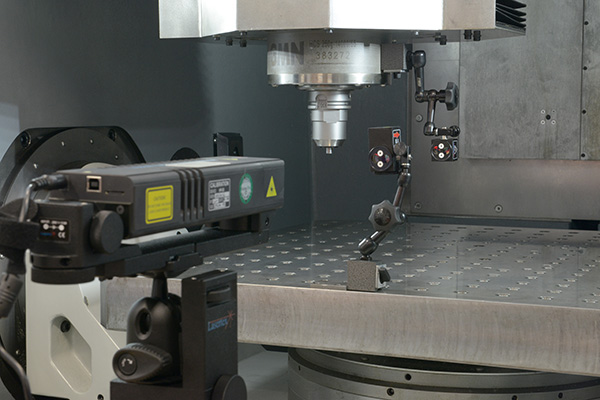
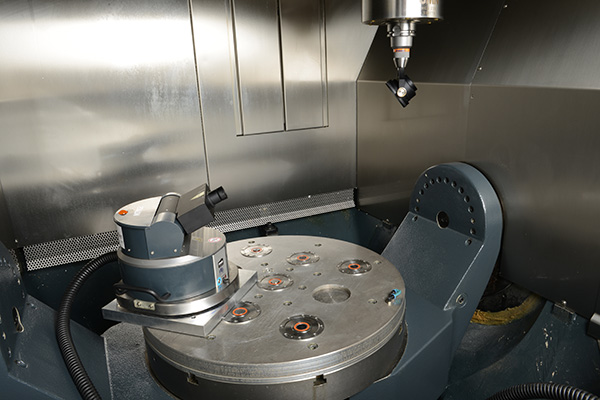
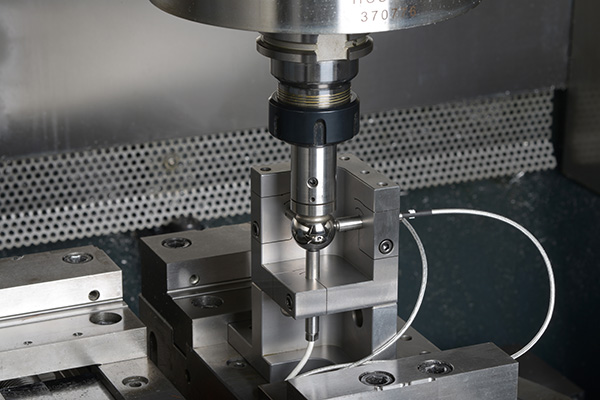
The precision of machine tools is extremely important for the manufacture of high-quality products used in various industries such as automotive engineering, aerospace engineering and medical technology.
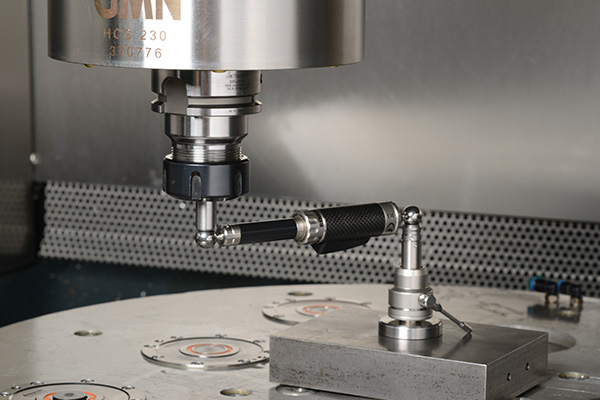
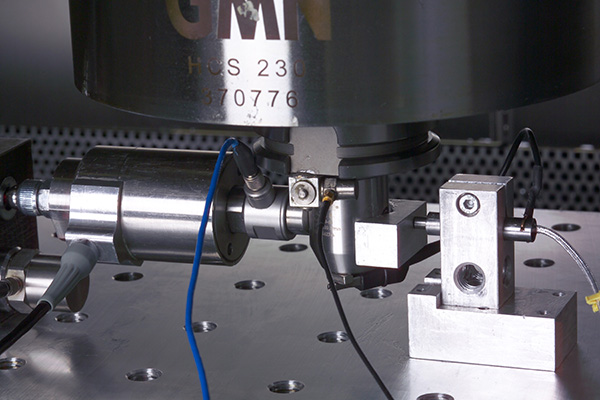
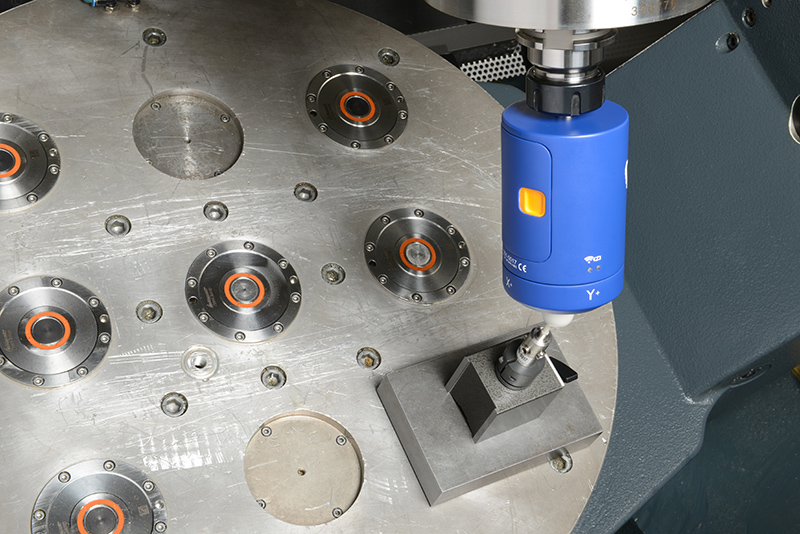
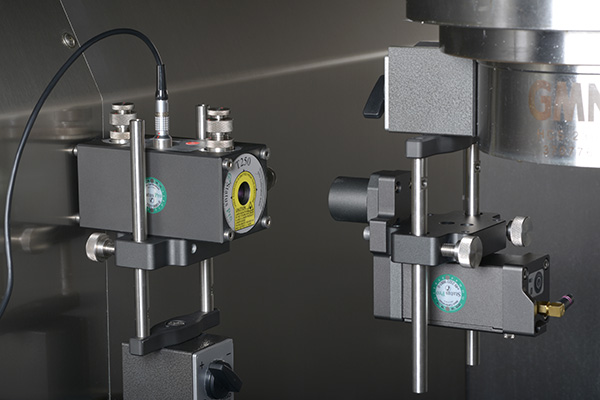
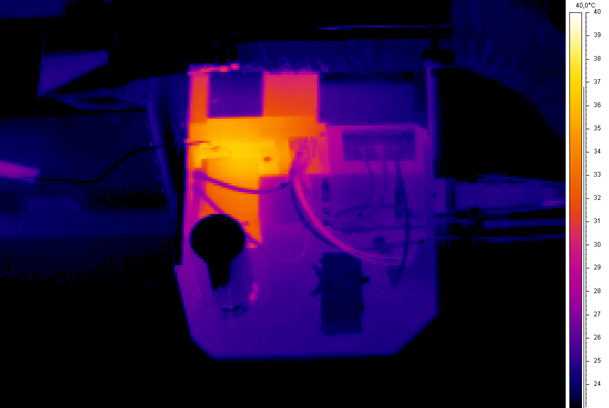
By using machine characterization tools, users can identify, analyze and optimize geometric, static, thermal and dynamic machine properties. Fraunhofer IPT has accumulated considerable expertise in this domain through extensive research over many years, and now possesses a comprehensive range of modern measuring instruments for investigating various machine types and kinematics.
Modern measuring instruments: The key to high-precision machines
Suitable measuring equipment helps to identify machine errors: Benefit from a variety of measuring instruments that provide you with the right tool for every use case. Take a look at our measuring equipment portfolio!
Deep process knowledge creates solutions
When machined parts suddenly go out of tolerance, machine operators often have no idea what caused the problem. Together with our customers, we develop methods to ensure high machine accuracy. We assist machine users in process optimization, as well as custom machine builders and machine manufacturers in the development of high-precision machine tools.
Our customer-specific services at a glance
- Machine characterization and optimization as a service (comprehensive on-site analysis)
- Software solutions & training for long-term customer empowerment
- Licensing of optimization methods for machine tool manufacturers